China has issued four national standards for toy safety:
Toys are an important product for children's consumption. Because of their skin sensitivity and lack of awareness, children are prone to accidental injuries when using toys. In order to protect the safety and quality of children's toys and protect children's personal health and safety, the National Standards Committee revised GB6675-2003 "National Toy Safety Technical Specifications" to form the national standard 1-4 of GB6675-2014 "Toy Safety". These include "Toy Safety Part 1: Basic Specifications," Toy Safety Part 2: Mechanical and Physical Properties, Toy Safety Part 3: Flammability, Toy Safety Part 4: Migration of Specific Elements, It will be enforced on January 1, 2016. Recently, the AQSIQ and the National Standards Committee issued these four national standards for toy safety. The new standards have made the protection of children more comprehensive and strict, and have made new progress in many aspects.
Standard overview
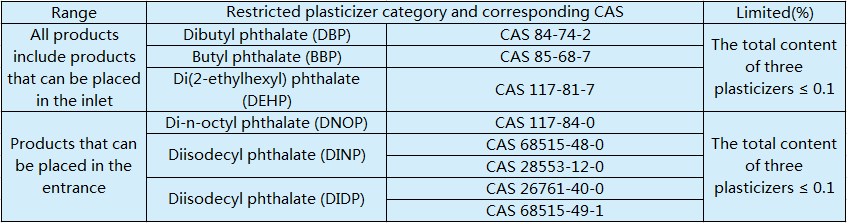
Children are the main consumer groups of toys, and China attaches great importance to toy quality and safety standards. According to Lu Chunming, deputy director of the General Office of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, as of now, there are 31 national toy standards in China. The 2003 edition of the National Toy Safety Technical Specification is the most basic and important national standard for toys. It stipulates the mandatory technical requirements for mechanical and physical properties, combustion properties, transferable chemical elements, markings and instructions that toy products must follow. Other national standards regulate the safety, performance and testing methods of baby carriages, cribs, cradle, infant pacifiers, plush and cloth toys. For example, GB/T9832-2007 "Plush, cloth toys" national standard was officially implemented on September 1, 2008, clearly requiring plush, cloth toys in the sewing quality must be even stitches, no off-line, jump needle , broken lines and other phenomena. On January 4, 2011, the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine and the National Standards Committee approved the release of GB/T26175-2010 "Test method for kinetic energy of catapult toys" and GB/T26193-2010 "Migable elements in toys, arsenic, antimony, cadmium, Determination of chromium, lead, mercury and selenium in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Two of the national standards, the former stipulates the method for testing the projectile kinetic energy of catapult toys, which was implemented on June 15, 2011; the latter specifies inductively coupled plasma. The method for the determination of migratory elements strontium, arsenic, antimony, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury and selenium in toy materials by mass spectrometry was carried out from June 1, 2011. The GB30004-2013 "Safety Requirements for Baby Cradle" national standard was released on October 10, 2013 and will be implemented on June 1, 2015. This standard specifies the safety technical requirements, test methods, identification and use of the baby cradle. Description.Table 1 defines plasticizer categories and limit requirements
The standard published this time is a revision of the 2003 edition of the National Toy Safety Technical Specification, which covers the basic safety of toys. It is understood that in accordance with the State Council's deployment of strengthening the technical standards system construction, the State Standards Commission has stepped up the implementation of the requirements for the revision of a group of urgently needed mandatory standards, and revised the "Toy Safety" into a series of standards for the purpose of ensuring safety and health. Part 1 is the basic specification to eliminate the safety "dead angle". Sections 2-4 are proposed as general safety requirements. Based on the first part, the hazard types of toy machinery and physical properties, flammability and specific element migration are proposed. More specific safety requirements and testing methods, technical indicators are more "close" applicable.
According to the staff of the National Standards Committee, GB6675.1-2014 "Toy Safety Part 1: Basic Specifications" is a basic specification for toys. The standards clarify the general safety and the qualitative requirements that do not allow any harm to children, and The specific safety requirements proposed by the national conditions, such as the limit requirements for plasticizers, * restrictions, etc.; the standard also clarifies the relevant measures for the enforcement of toy safety standards, including national compulsory certification, supervision and spot checks, recalls, etc. The standard states: Units and individuals engaged in toy research, production, and operation shall strictly implement this part, products that do not conform to this part, and prohibit production, sale, and import; state organs, enterprises, and all citizens have the right to report, appeal, The complaint violates the behavior of this part; the state implements the supervision and inspection system based on the spot check as the main method for the quality of toys (products); for the toys of the same nature that jeopardize the unreasonable dangers of children's health and safety, according to the "Children's Toys Recall Management Regulations" "carried out.
GB6675.2-2014 "Toy Safety Part 2: Mechanical and Physical Properties", GB6675.3-2014 "Toy Safety Part 3: Flammability", GB6675.4-2014 "Toy Safety Part 4: Specific Elements Migration is a general safety requirement for toy machinery and physical properties, flammability, and migration of specific elements. These three standards are developed for the qualitative requirements of GB6675.1, including limit values and detection methods.
Among them, "Toy Safety Part 2: Mechanical and Physical Properties" specifies the requirements for acceptable toy structural features, including shape, size, contour, clearance (such as rattle toys, small parts, sharp tips, sharp edges, hinges, etc.) And some parameters of the performance of the toy, such as the maximum kinetic energy of the non-elastic head projectile, the minimum tilt angle of some riding toys, and so on. "Toy Safety Part 3: Flammability" specifies the categories of flammable materials that are prohibited for use on all toys and the flammability requirements of certain toys that may come into contact with small sources of ignition. "Toy Safety Part 4: Migration of Specific Elements" specifies the maximum requirements, sampling methods, and tests for migratory elements in toys and toy parts - bismuth, arsenic, antimony, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury, and selenium. Sample preparation and extraction procedures.
Major change
Lu Chunming pointed out that the new standard is more comprehensive and strict for children. The new version of the "Toy Safety" series of national standards takes safety as the core goal, expands the scope of application of the standard, and tightens the requirements for safety indicators such as sound, mechanical parts and combustion performance. For the plasticizers of public concern, the new standard also lists six plasticizers such as dibutyl phthalate (DBP) as restricted substances, and the limit requirements are the same as those in the EU. The main changes in the new standard include the following:
First, the scope of application is more clear. GB6675.1-2014 "Toy Safety Part 1: Basic Specifications" clarifies that the standard is applicable to toys and materials designed or intended for use by children under 14 years old, as well as for toys that are not specially designed for play but have play function. Products intended for children under the age of 14, that is, for children under the age of 14 and having playful functions, should meet the requirements of this standard.
The second is to increase the requirements for six plasticizers such as DBP, BBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP, DIDP, etc. The limit values of the six plasticizers shall not exceed the limit requirements specified in Table 1 (see table below). This limit is equivalent to the current EU regulations.
Third, the requirements for sound are more stringent. In order to protect the hearing of children, especially babies, GB 6675.2-2014 "Toy Safety Part 2: Mechanical and Physical Properties" lists the sound requirements as mandatory and tightens some of the limits, such as the continuous production of near-ear toys. The A-weighted equivalent sound pressure level LpAeq of the sound should not exceed 65 dB.
Fourth, the requirements for magnets and magnetic components have been added. GB6675.2-2014 "Toy Safety Part 2: Mechanical and Physical Properties" has added magnet and magnetic component requirements to prevent magnetic materials or components from being swallowed by children and causing injury.
The fifth is to improve the requirements for combustion performance. In order to prevent possible burning damage from toys, GB6675.3-2014 "Toy Safety Part 3: Flammability" adds "all or part of the molded mask" and "the ethereal on the toy" to the easy fire. The burning rate is required. At the same time, different test methods are specified for the size specifications of the soft-filled toy. The new test method can more accurately test the burning speed of the toy to determine the safe burning performance of the toy.
The sixth is to widen the control range of harmful substances. GB6675.4-2014 "Toy Safety Part 4: Migration of Specific Elements" adds provisions for accessible coatings and accessible liquids, pastes and gels (eg liquid paints, modeling compounds) to reduce harmful substances Possible harm to children.
With international standards
It is understood that the International Organization for Standardization / Toy Safety Technical Committee (ISO / TC181) is responsible for the development of international standards for toy safety, the technical committee including 24 members of China, the United States, Japan, etc., formulated and issued the ISO8124 "Toy Safety" series of standards. GB6675-2014 "Toy Safety" 1-4 part is based on the reference of ISO8124 standard, the main technical indicators are consistent with ISO8124, and the plasticizer limit requirements are increased compared with ISO8124.
Lu Chunming introduced that the standard revision reflects the principle of international integration and extensive participation. Based on China's national conditions, the new standard refers to the international standard ISO8124 "Toy Safety" and draws on relevant EU directives and standards. During the revision process, opinions from relevant parties were widely heard to ensure that the procedures were fair, equitable and scientific. At the same time, standard revision is also a useful exploration of mandatory standards reform. 中文
中文  中文
中文 
